Amaplast - the national trade association, member of Confindustria, of over 160 Italian manufacturers of plastics and rubber processing machinery, equipment, and moulds - held its annual member Assembly on Wednesday, September 16, 2020, at Villa Borromeo in Cassano d’Adda (Milan, Italy).
The assembly also provided the opportunity to celebrate Amaplast’s sixtieth anniversary, an important milestone for an organization that represents one of the preeminent segments of the mechanical engineering industry in Italy. Some of the companies that took part in founding the association on September 27, 1960, are still active members, flanked by others who have joined over the decades and strengthened its identity. Amaplast President Dario Previero made a point of emphasizing that this anniversary does not represent a point of arrival, but an intermediate stage, with the objective to continue growing in an increasingly competitive and globalized market.
The new Articles of Incorporation were approved during the assembly, aligning with the new unified regulations for the Confindustria system, and the Amaplast associative bodies were new-ly elected:
- Board of Directors, with the election of Michele Bandera (Bandera), Maria Grazia Colombo (BFM), Gianni Luoni (Elba), Alessandro Balzanelli (FB Balzanelli), Barbara Ulcelli (IMG), Luciano Gallino (Maris), Claudia Persico (Persico), Gianfranco Cattapan (Plastic Systems), Corrado Zanga (Uniloy Italia), for a two-year term in 2020-2022;
- Board of Arbitrators, with the election of Andrea Mariani (Hnnecke-OMS), Simone Maccagnan (MacGi), Maurizio Toniato (Mobert), Flavio Giordani (Plastiblow), and Romeo Varisco (Termostampi), and Board of Auditors, with the election of Gianni Cazzulo (chartered accountant), Claudia Cribiù (Crizaf), Roberta Rivi (Rivi Magnetics), for four-year terms in 2020-2024.
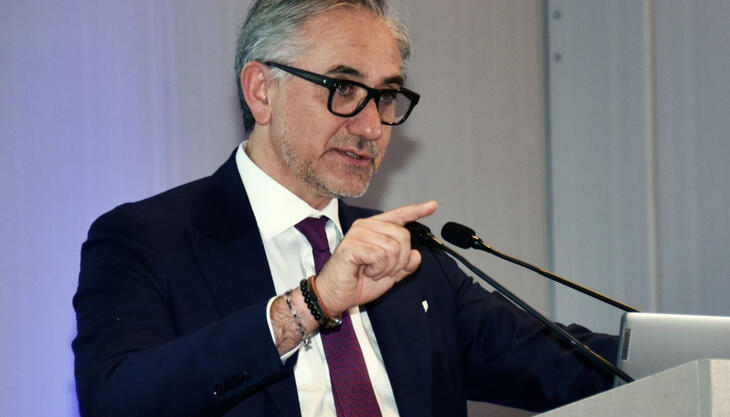
In his speech, President Dario Previero illustrated the performance of the Italian plastics and rubber processing machinery, equipment, and moulds industry, commenting on the reports by the Amaplast Statistical Studies Center and acknowledging that the eight-year upward trend for the industry had come to halt and that 2019 had closed negatively.
President Previero also mentioned the synergetic project that Amaplast has recently undertaken with Acimac (Association of Italian Manufacturers of Machinery and Equipment for Ceramics) and Ucima (Italian Packaging Machinery Manufacturers Association). The project will make it possible to further improve the quality of services offered to member companies (from credit and finance to training, from technical issues to promotion, and much more), sharing the competencies, services, and experience of each.
A report was presented during the public session after the Assembly titled “Millennials: a genera-tion without a future… and without plastic?” Of great current relevance, it focuses on the new generations, what they think, how they move, and their opinions on plastic. This was followed by a round-table discussion “Plastic: its future in a circular world”. The event concluded with a gala dinner to celebrate the association’s 60th anniversary and a show by the Italian comedian Andrea Pucci.
Sector data
In his speech, Amaplast President Dario Previero illustrated the performance of the Italian plastics and rubber processing machinery, equipment, and moulds industry, commenting on the reports by the Amaplast Statistical Studies Center and acknowledging that the eight-year upward trend for the industry had come to halt and that 2019 had closed with all indicators in the red.
The signs of an imminent reversal of trend had begun to be seen at the end of 2018, when growth in production was fractional and exports had already begun to decline, albeit only slightly.
During the following year, the trend in foreign trade remained constantly negative, especially as regards imports, although the downturn at the end of 2019 was not as bad as had been feared.
In any case, the 2019 balance for Italian manufacturers is in line with that of their German competitors, who recorded a drop of 5% in imports and 7% in exports.
A host of economic and commercial uncertainties came one after another or overlapped during the final months of 2019, putting a chill on domestic investment, partly attributable to the drying up of Industry 4.0 effects and changes in the dynamics of Italian exports for the sector, which, on the average, continue to represent approximately 70% of production.
President Previero underscored the fact that, on the average, Amaplast member companies suf-fered less than the rest of the industry, with a drop in revenues on the order of 5% and of ex-ports of 2.5%.
 Of course, this was the situation prior to the Covid-19 emergency, where Italy and the rest of the world were suddenly forced to cope with an unprecedented situation.
Of course, this was the situation prior to the Covid-19 emergency, where Italy and the rest of the world were suddenly forced to cope with an unprecedented situation.
It is difficult to make projections as to how the crisis will proceed, much less what impact it will have on Italian manufacturers of plastics and rubber processing machinery.
On the basis of studies undertaken by the association, accounting for the variables that characterize the sector, it is expected that the current year will close with a reduction in orders of 20-25%.
VDMA, the association representing the German competitors, has forecast a similar contraction in orders, even adjusting the figure last month (August 2020) to -30%.
Istat statistics for Italian foreign trade in the sector in the first half of 2020 show double-digit drops in both trade flows compared to the same period in 2019: -17.6% for imports and -21.7% for exports. However, this represents a slight improvement with respect to data for May, when the respective figures were over 18% and approaching 23%.
 This mid-year balance certainly comes as no surprise given the complex economic context in which Italian machinery manufacturers have to operate, given the pandemic. But the slight reversal of trend may corroborate the latest forecasts by Istat and Confindustria, together with other organizations, which detect in the last few weeks some recovery (albeit small) for Italian industrial production in a situation that is still very complicated.
This mid-year balance certainly comes as no surprise given the complex economic context in which Italian machinery manufacturers have to operate, given the pandemic. But the slight reversal of trend may corroborate the latest forecasts by Istat and Confindustria, together with other organizations, which detect in the last few weeks some recovery (albeit small) for Italian industrial production in a situation that is still very complicated.
A look at the macro-geography of Italian exports for the sector provides little comfort, with the historically principal outlet markets showing double-digit declines:
- -20% in Europe. Significant within the European Union are the -17% for Germany and Poland, and figures in the neighbourhood of -30% for Spain, France, and the United Kingdom;
- -28% in the Middle East and -23% in the Far East. While the major Middle Eastern markets have substantially held their ground (Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Israel, with Iran having declined in importance for some time now) the minor ones have collapsed. As for the rest of Asia, the negative performance of China and Indonesia weighs heavily, while India has held firm;
- -26% in North America, where the previous constant growth of trade with the United States witnessed an abrupt halt and Mexico and Canada continue their slide;
- -31% in South America, dragged down by Brazil, Argentina, and Colombia;
- -13% in Africa, with countries in the north outperforming the rest of the continent. Overall, suffering most were exports to the historically most important African countries for Italian machinery manufacturers.