A two-faced molecule for innovative polymers
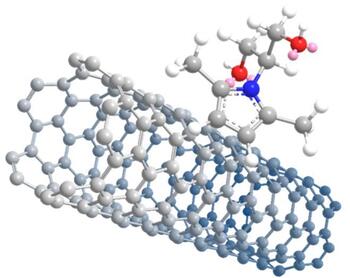
The Politecnico di Milano patented a new molecule that can attach in a stable manner to various forms of carbon, such as carbon black, graphite, nanotubes and graphene, which provide increased mechanical strength and electrical and thermal conductivity. These types of carbon become soluble in polar solvents such as water, in addition to dissolving in low environmental impact solvents and in different kinds of polymers, without compromising traditional compatibility with non-polar matrices.
It is extremely simple to prepare the molecule, as no solvents or catalyzers are required and the only by-product is water. The yield is very high (95% at least) and ensures atom efficiency above 80%. The starting compound is serinol, a naturally available derivative of glycerine.
The molecule's key feature is its two-faced nature, which allows it to be soluble in water and, at the same time, to interact stably with carbon-only based substances.
In this simple molecule there are functional groups that can polymerize in a number of ways. Innovative polymers can be obtained in this manner, such as polyurethanes, which are ideal binders for carbon fillers in composite materials with advanced properties.
The great advantage of the Politecnico's invention is that stable adducts with any of the forms of carbon mentioned above can be obtained by simply mixing. There is no need for the expensive (and sometimes dangerous) chemical reactions that are currently required and are performed with invasive chemical agents. In particular, it is easier in this way to use carbon nanofillers, nanotubes and graphene, the latest frontier of research in the field of high performing materials.
There are many applications for this invention. In dispersions for the treatment of surfaces, inks especially, it provides electrical conductivity to transparent layers, which could be invisible because of the small quantity of carbon substances. In thermoplastic and elastomeric polymer composites, mechanical properties, electric conductivity, resistance to heat and flame are greatly enhanced, thanks to improved dispersion and the intimate interaction of the carbon fillers with the matrix. It is important to underline that the adhesion of the fillers to the polymeric matrix allows the use of the composite material for challenging mechanical and dynamic applications such as mixtures for tyres.
The stable interaction of the nanofillers with the polymeric matrices is crucial for the prevention of dispersion into the environment, thus avoiding the related issues.
This invention makes it possible to work not just on improving the performance of existing materials but on obtaining new generations of materials and levels of performance as well.